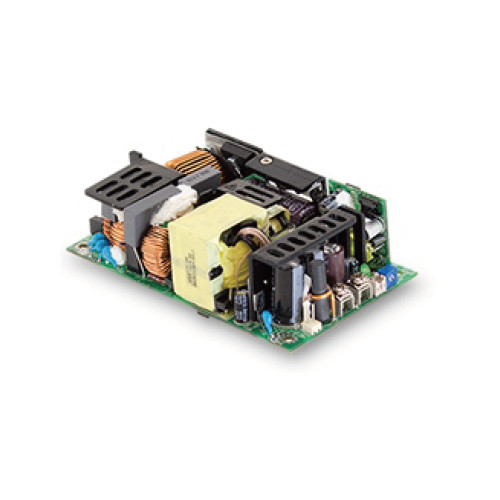
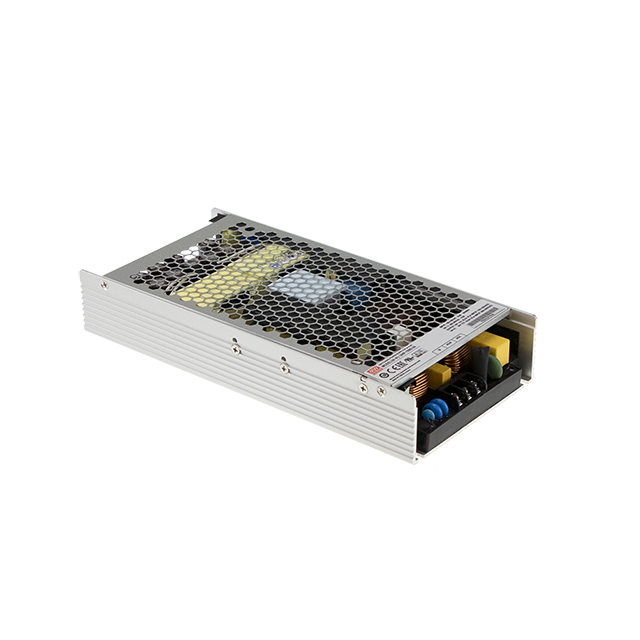
What is a Circuit board power supply?
Have you ever wondered what a PCB power supply actually is? In this article, we’ll explain everything you need to know about it. A PCB power supply is a type of power converter used in a variety of electronic devices. It is a complex unit that converts the alternating current (AC) from the wall outlet into the direct current (DC) required by electronics. Such a power supply consists of various components mounted on a printed circuit board (PCB), including resistors, capacitors, and transistors. These components work together to ensure a stable, regulated current flow that enables electronic devices to operate smoothly. PCB power supplies are generally more efficient and reliable than conventional power supplies because they are specifically designed for use within electronic equipment. Whether you’re a tech-savvy hobbyist or simply want to understand how your electronic devices work, this article will give you a thorough introduction to the world of PCB power supplies—so you can better grasp how this vital component functions.
What is a PCB Power Supply?
A PCB power supply is a specialized type of power converter designed to transform alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) in electronic devices. It is an integrated system mounted on a printed circuit board, which houses various electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and transistors. These parts play a crucial role in regulating and stabilizing the electrical energy delivered to connected devices. By performing this conversion, the PCB power supply ensures that sensitive electronics receive the correct voltage and current. Typically, PCB power supplies employ advanced circuit techniques to achieve high efficiency and reliability. The use of quality materials and modern technologies allows these power supplies to remain stable even under changing conditions. Their compact design makes it possible to integrate them into a wide range of devices, from computers and televisions to medical equipment. In many cases, PCB power supplies also include protection mechanisms that guard against overloads or short circuits.
The ongoing trend toward miniaturization in electronics has driven the development of PCB power supplies; they are not only space-saving but also lightweight and powerful, making them a preferred choice in modern electronics. In the sections that follow, we will delve into the various functions, advantages, and applications of PCB power supplies.
Functions of a PCB Power Supply
The primary function of a PCB power supply is to convert alternating current into direct current. This conversion is essential because most electronic components—such as microprocessors and memory chips—require DC to operate correctly. The process typically involves multiple steps, beginning with rectification of the AC and followed by smoothing to achieve the desired DC quality. These steps are necessary to provide a stable, clean power source for connected devices. Another key function of a PCB power supply is voltage regulation. These power supplies are designed to deliver a constant output voltage required by the devices they power. Feedback control circuits monitor the voltage and make adjustments to avoid sudden fluctuations. Such regulation is particularly important in applications where power stability is critical to device performance and longevity. In addition to these core functions, many PCB power supplies incorporate protection features that prevent overcurrent, overvoltage, or overheating from damaging connected devices. These safeguards often take the form of fuses or electronic protection circuits that activate when needed to interrupt power delivery. Through these measures, PCB power supplies enhance the safety and reliability of electronic systems.
Differences Between a PCB Power Supply and a Conventional Power Supply
The main differences lie in construction and performance. Conventional power supplies are often separate units enclosed in metal casings, whereas PCB power supplies are mounted directly on a circuit board. This compact layout allows for more efficient use of space and simpler integration into electronic devices.
Efficiency is another significant difference. PCB power supplies usually employ modern circuitry that minimizes energy loss, achieving higher efficiencies than conventional units. Traditional power supplies tend to generate more heat, making them less energy-efficient. In an era of rising energy costs and environmental awareness, the efficiency of power converters has a substantial impact on overall energy consumption.
Finally, PCB power supplies often include additional functions and protection mechanisms—such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and temperature monitoring—that may be absent in conventional models. These safety features increase reliability and extend the lifespan of connected devices, which is essential in many modern applications.
Advantages of a PCB Power Supply
PCB power supplies offer numerous advantages that make them the preferred choice in the electronics industry. One key benefit is their high efficiency. By using advanced technologies and circuit designs, these power supplies often achieve efficiencies above 90%, reducing energy waste and lowering operating costs. Their compact form factor is another major advantage. Because PCB power supplies are mounted on a board, they take up significantly less space than traditional units. This is especially valuable in applications where space is at a premium, such as portable devices or automotive electronics. The small size also allows designers to pack more functionality into a smaller footprint, increasing design flexibility. PCB power supplies also deliver enhanced reliability. Their rugged construction and built-in protection features make them less prone to failure. This reliability is critical in sensitive applications, such as medical devices or aerospace systems, where uninterrupted power delivery is essential. The durability and dependability of PCB power supplies therefore contribute significantly to the overall quality of the electronic systems they support.
Applications of a PCB Power Supply PCB power supplies are used in a wide array of applications, from everyday household gadgets to complex industrial systems. One of the most common uses is in computers, where they provide the multiple voltage rails needed by the motherboard, graphics cards, and other components. The ability to supply several output voltages makes PCB power supplies ideal for modern PC architectures. Another major application area is consumer electronics. Televisions, audio/video equipment, and gaming consoles all rely on PCB power supplies for stable and efficient operation. These devices often require multiple voltage levels to drive their internal circuits, making PCB solutions particularly suitable. In industrial settings, PCB power supplies are found in control systems, robotics, and automation equipment. Here, high efficiency and reliability are vital, as power failures can lead to significant production losses. In medical technology, PCB power supplies are crucial for delivering precise and stable voltages needed for accurate measurements and treatments.
Selection Criteria for a PCB Power Supply
When choosing a PCB power supply, several factors must be considered to ensure it meets the demands of the intended application. First, output voltage is critical. The selected supply must provide the correct voltage for connected devices. Since different components often need different voltages, multi-output supplies can be advantageous. Next, maximum output power should be evaluated. Each electronic system has a specific power requirement, and the PCB supply must deliver enough current without overloading. It’s advisable to choose a supply with a power rating slightly above actual needs to prevent overheating and premature wear. Efficiency and protection features are also key considerations. High efficiency reduces energy consumption and heat generation, while built-in safeguards—such as overcurrent, overvoltage, and thermal protection—ensure device safety. Careful attention to these criteria will maximize the lifespan and reliability of the PCB power supply.
Installation and Wiring of a PCB Power Supply
Proper installation and wiring are essential for safe and reliable operation. First, prepare the mounting area, ensuring ample space and adequate ventilation to prevent overheating. Then select appropriate cable types and sizes capable of handling the supply’s maximum current. Wires should be routed to avoid contact with other components, reducing the risk of shorts. Organized wiring also simplifies future maintenance and troubleshooting. After installation, test the supply with a multimeter to verify output voltages against specifications. Once confirmed, perform a load test to ensure stable performance under real-world conditions. Maintenance of a PCB Power Supply
Regular upkeep is crucial for long-term performance. Dust accumulation can impede cooling and lead to overheating, so periodic cleaning—using compressed air if needed—is recommended. Inspect electrical connections for looseness or corrosion, and replace any damaged wires to maintain efficient operation. Monitor the supply for signs of stress, such as voltage drops or unusual noises. Addressing these issues promptly—or replacing the unit if necessary—helps prevent damage to connected electronics. Proactive maintenance ensures the safety and reliability of the entire system.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount when working with PCB power supplies. Ensure the unit meets relevant certifications (e.g., CE, UL, TÜV) that attest to rigorous safety testing. Proper grounding is essential to prevent hazardous voltages during faults; check earth connections regularly for security and integrity. Avoid overloading by selecting a supply with sufficient capacity for the total load. Adhering to these safety practices greatly reduces the risk of accidents and equipment damage.